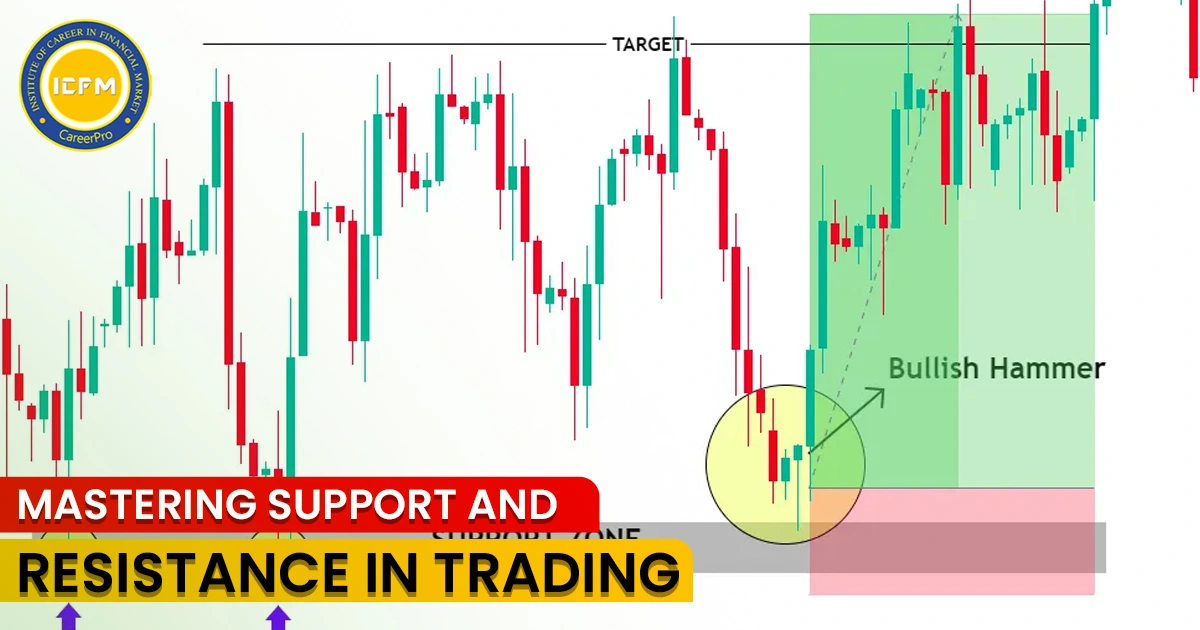
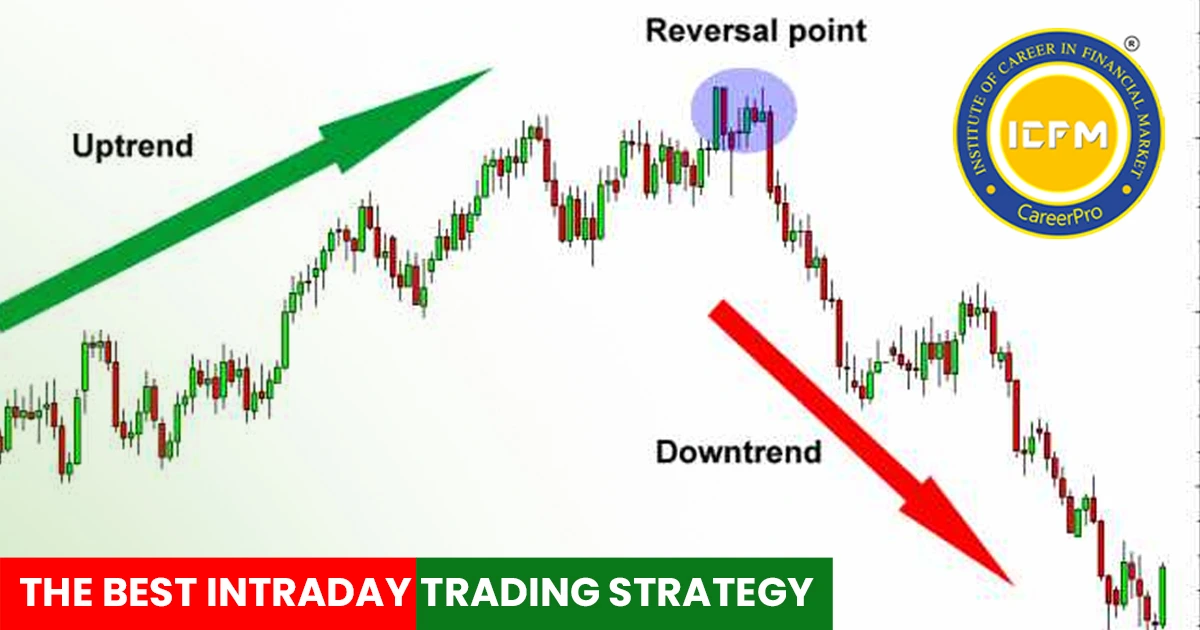
Derivatives trading has great profit-making potential but with its share of risks. Many traders, especially beginners, tend to commit mistakes that may bring in massive losses. In this section, we outline some of the most common mistakes in derivatives trading and how to avoid them.
1. Lack of Proper Knowledge
a. Mistake:
Entering derivatives trading without knowledge of the instruments-futures and options and their intricacies.
b. Why It's a Problem:
Derivatives are leveraged instruments, and a lack of understanding can amplify losses. For example, not knowing the difference between a call and a put option can lead to misplaced trades.
c. How to Avoid:
- Learn the basics of derivatives trading, including key terms like moneyness, Greeks, and margin.
- Take certified courses like NISM Derivatives Certification.
- Practice trading on a simulated platform before using real money.
2. Ignoring Risk Management
a. Mistake:
Failure to set stop-loss levels or failure to apply proper position sizing.
b. Why It's a Problem:
Without risk management, a single trade can wipe out your entire capital due to the leverage involved.
c. How to Avoid:
- Always use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses.
- Follow the 2% Rule: Do not risk more than 2% of your capital on a single trade.
- Diversify your portfolio to spread risk.
3. Overleveraging
a. Mistake:
Taking oversized positions by utilizing full leverage provided by brokers.
b. Why It’s a Problem:
While leverage can amplify profits, it can also magnify losses, leading to margin calls or forced liquidation.
c. How to Avoid:
- Use leverage judiciously; trade within your financial limits.
- Maintain sufficient margin in your trading account to avoid forced square-offs.
- Start with smaller positions and increase gradually as you gain experience.
4. Neglecting Volatility
a. Mistake:
Entering trades without accounting for volatility or ignoring implied volatility in options trading.
b. Why It's a Problem:
Volatility affects the pricing of options. High IV causes an inflation of option premiums, while low IV may cause undervalued options.
c. How to Avoid:
- Study the Implied Volatility (IV) before entering a trade-in options.
- Utilize strategies like Iron Condor or Straddle and take advantage of certain conditions of volatility.
- Be watchful of any event that may create sharp volatility spikes, such as earnings announcements or budget days.
5. Holding Losers
a. Mistake:
Never close a losing trade hoping the market will turn around for you.
b. Why It's a Problem:
The longer you hold a losing position, the bigger the potential loss, especially in derivatives with an expiration date.
c. How to Avoid
- Keep the stop-loss levels as planned.
- Accept losses as part of trading and move on to the next opportunity.
- Avoid emotional attachment to trades.
6. Overtrading
a. Mistake:
Making multiple trades in a short period is often driven by greed or the need to recover losses.
b. Why It’s a Problem:
Overtrading leads to higher transaction costs and can drain your mental energy, resulting in poor decision-making.
c. How to Avoid:
- Trade only when you have a clear strategy and setup.
- Limit the number of trades per day or week.
- Focus on quality over quantity.
7. Misunderstanding Option Greeks
a. Mistake:
Ignoring the role of Greeks like Delta, Gamma, Theta, and Vega in option pricing and risk assessment.
b. Why It’s a Problem:
Without understanding the Greeks, traders may misjudge the risk-reward of an options strategy. For example, ignoring Theta can lead to unexpected losses in time decay.
c. How to Avoid:
- Study the impact of each Greek on option pricing.
- Use Delta-neutral strategies if you aim to hedge against price movements.
- Monitor your portfolio’s sensitivity to time decay and volatility.
8. Chasing Market Trends
a. Mistake:
Blindly following market trends or recommendations without doing your research.
b. Why It’s a Problem:
Trends can reverse quickly, and recommendations may not suit your risk appetite or trading goals.
c. How to Avoid:
- Conduct your analysis before taking any trade.
- Use technical indicators like moving averages or RSI to validate trends.
- Avoid FOMO (Fear of Missing Out).
9. Ignoring Expiry Dates
a. Mistake: Not paying attention to the expiry date of derivative contracts can lead to forced square-offs or delivery obligations.
b. Why It’s a Problem: Options become worthless if they expire from the money (OTM). Futures can lead to huge losses if held to expiry.
c. How to Avoid:
. Monitor the expiry dates for all your contracts.
. Get out of your positions well ahead of time if you're not rolling or taking delivery.
10. No Trading Plan
a. Mistake:
Trading without a set plan and using intuition or tips as the guide.
b. Why It's a Problem:
The absence of a plan can cause you to have inconsistent results and make emotional trades.
c. How to Avoid It:
- Create a detailed trading plan that involves entry and exit rules, risk management, and capital usage.
- Hold fast to the plan even in a volatile environment.
- Review and refine your plan based on performance regularly.
Conclusion
Avoiding these common mistakes can significantly enhance your chances of success in derivatives trading. Always prioritize knowledge, discipline, and risk management over short-term profits. Remember, derivatives are powerful tools, but their effectiveness depends on how well you use them.