Option Chain: A Trader's Complete Guide
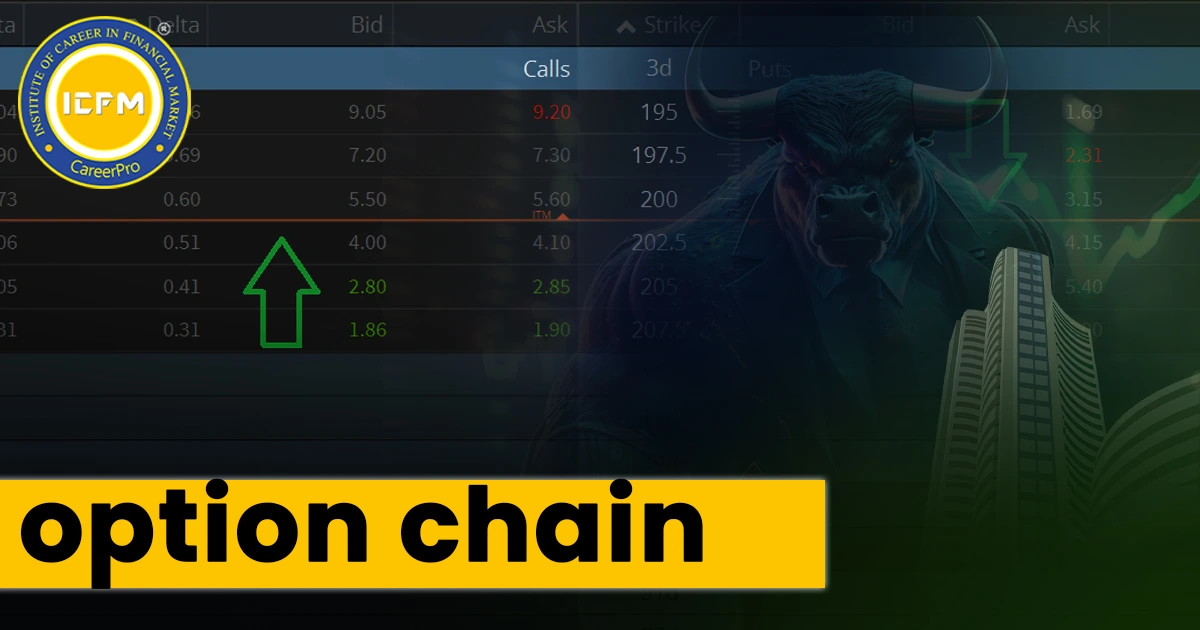
An option chain is an important tool for options traders, as it shows all available options contracts for a specific security and a given expiration date. It is presented in a detailed format according to strike price, volume, open interest, implied volatility, and many other fields, making it a complete source for informed trading decisions.
Anyone interested in becoming a successful options trader needs to learn how to read and understand the analysis of an option chain. We are going to learn what comprises an option chain, its usage, and the reasons it is important so we can make better trading decisions.
What is an Option Chain?
An option chain is a tabular representation of options contracts, which are divided into two major categories: calls and puts, and are separated by the strike price column. It gives all the information about an option, including:
Open Interest (OI)
Change in OI
Implied Volatility (IV)
Last Traded Price (LTP)
Bid Price & Quantity
Ask Price & Quantity
This information helps traders gauge the market sentiment, liquidity, and volatility while finding potential support and resistance levels.
Significance of Options Chain Analysis
1. Identifying ITM, ATM, and OTM Options
The option chain identifies which options are In-The-Money (ITM), At-The-Money (ATM), or Out-of-The-Money (OTM).
ITM Options: They have an intrinsic value.
ATM Options: The strike price is equivalent to the current market price.
OTM Options: They have no intrinsic value.
2. Measuring Liquidity
Traders can gauge the trading activity of various strike prices. High volume and open interest show better liquidity, and it will be easier to enter or exit trades.
3. Market Sentiment
Open interest and its change help traders determine whether the market is bullish, bearish, or neutral.
4. Calculating Implied Volatility (IV)
IV reflects the market's expectation of price action.
High IV: Greater price action.
Low IV: Stable market.
5. Creating Advanced Strategies
Option traders use the chain to come up with strategies that help them build spreads, straddles, or strangles based on market conditions and risk appetite.
How to Read an Options Chain?
Key Elements:
Strike Price: This is the price at which the option can be exercised.
Less than the current price: In-the-money for calls, out-of-the-money for puts.
More than the current price: Out-of-the-money for calls, in-the-money for puts.
Open Interest (OI): This is the number of outstanding contracts at a given strike price. The higher the OI, the more interest from traders, and thus the greater support or resistance.
Change in OI: This reflects the day-to-day change in open interest, which reveals how positions are changing.
Volume: Indicates how many contracts are traded in a particular time frame, thus guiding traders about the current activity within the markets.
Implied Volatility (IV): The indicator of the expected price variation and the prevailing market mood.
LTP (Last Traded Price): The latest price through which the option is traded
Bid/Ask Price and Quantity:
Bid Price: the highest price a buyer is ready to pay
Ask Price: lowest price a seller accepts.
Bid/Ask Quantity: Number of contracts outstanding at the price of the bid/ask.
Net Change: Absolute change in LTP over the prior day. Indicates if the market is trending higher or lower.
Utilisation of Option Chain Information
1. Level of Support and Resistance
Strike prices with more OI are potential points of support and resistance.
2. Analysis of Market Psychology
An exchange can make sense if the market has a bullish or bearish trend by analysing variations in the OI of options at different strike prices.
3. Strategy Development
Option chains enable traders to develop strategies such as bull spreads, bear spreads, straddles, and strangles based on the prevailing market conditions.
4. Risk Management
Option chains provide information on Greeks (Delta, Theta, Gamma, Vega), enabling traders to manage their portfolios properly.
5. Hedging
Traders can hedge their existing positions by studying the liquidity and volatility of particular options.
Hope you liked the blog, will meet in another interesting blog.