Why the Risk-to-Reward Ratio in Technical Analysis Is Important
1. Safety of Trading against Losses - the risk-to-reward ratio works towards securing an eventuality that although there may be a row of failures, you are to reap better off in the long end, a strategy with a risk/reward ratio of 1:3 and a winning percent of 40, this results into a profit since there's an abundance in reward than risk.
2. Enhances Decision Making—It gives a clear framework for determining whether a trade is worth taking. If the potential reward is too low relative to the risk, it may not be wise to enter that trade, even if the technical analysis suggests a high probability of success.
3 Promotes Discipline - Trading without a defined risk-to-reward ratio can lead to impulsive decisions and emotional trading. Having a predefined risk-to-reward ratio forces traders to stick to their plan and avoid chasing the market.
Calculating the risk-to-reward ratio involves understanding your entry price, stop-loss level (where you're willing to cut losses), and target price (where you aim to make a profit).
• Distance from Entry to Stop-Loss: This is the amount you're risking per trade, often measured in pips or points on the chart.
• Distance from Entry to Target: The potential reward is measured in pips or points.
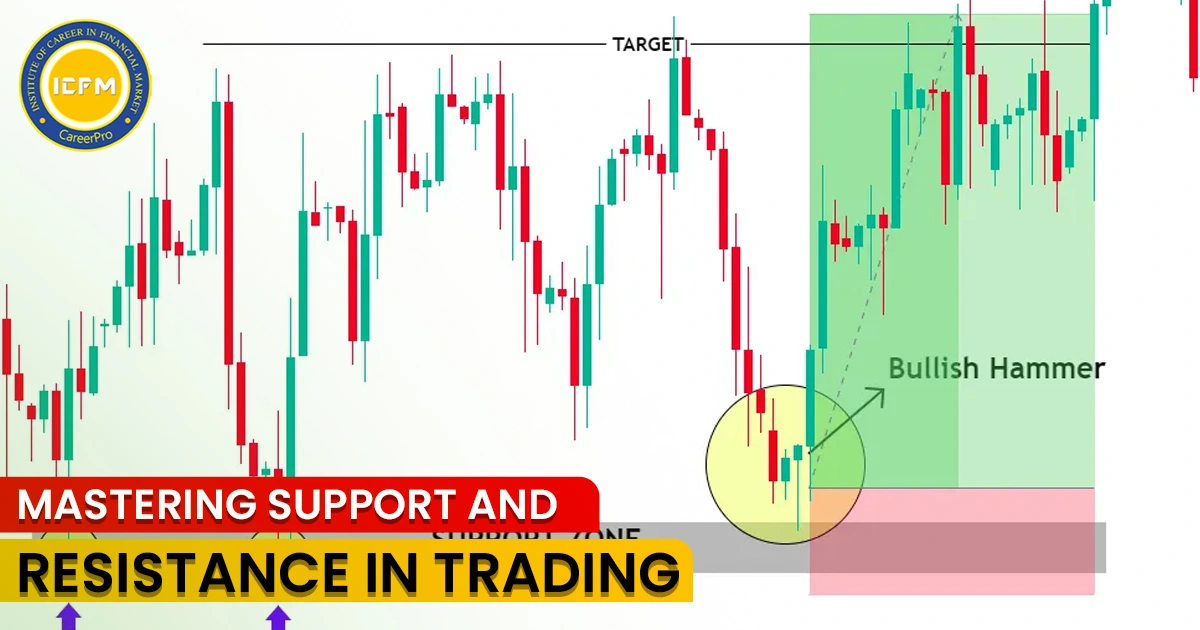
Set Clear Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels—Before entering a trade, you should determine your stop-loss and take-profit levels based on the chart. These levels should be placed in logical areas using technical analysis tools such as support and resistance zones, Fibonacci retracements, or moving averages.
Use Support and Resistance Levels to Set Stop-Losses - Identify support and resistance levels in your charts and place your stop-loss just beyond these levels. This reduces the chances of being stopped by normal market fluctuations. If your stop-loss is too tight, you risk getting stopped out too early, and if it is too wide, you increase your risk exposure unnecessarily.
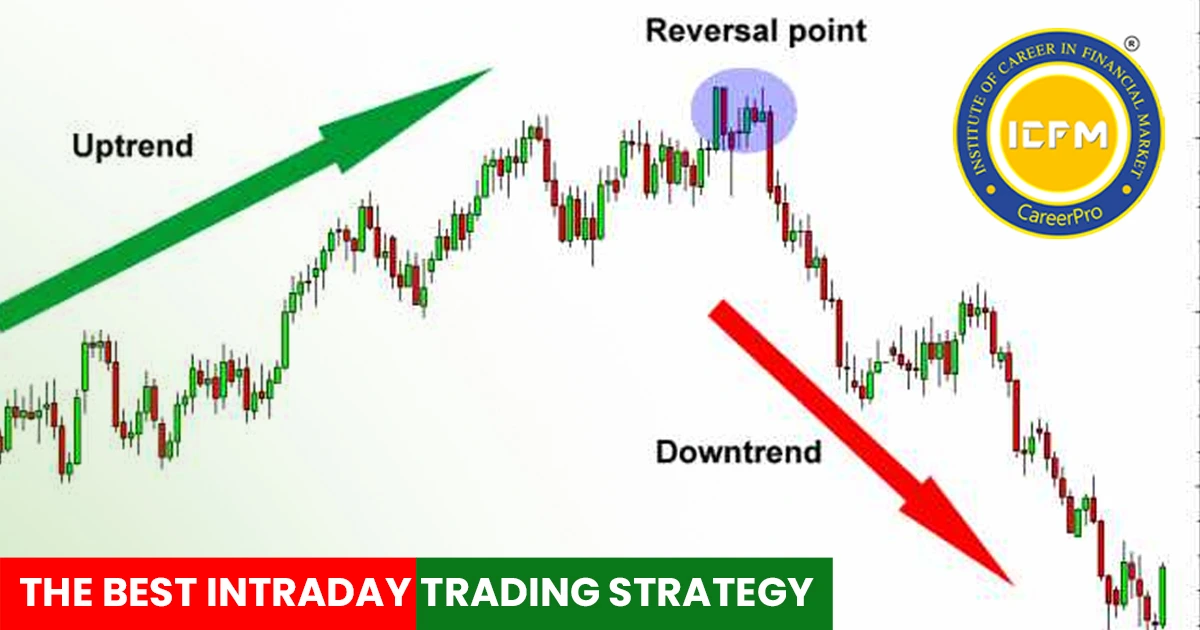
1. Set Realistic Profit Targets - Profit targets should also be based on technical analysis. Look for areas where the price might reverse, such as strong resistance levels or trendline breaks. Reward that is justifiable for the risk you are taking.
2. Risk Management and Position Sizing - Now that you have your risk-to-reward ratio, you can calculate the position size that is aligned with your overall risk tolerance. For example, if you're risking $100 on a trade (using your stop-loss) and have a 1:2 risk-to-reward ratio, your profit target will be $200. Your position size can then be calculated so you don't end up risking more than some set percentage of your trading capital, 1-2%.
3. Adjust for Market Conditions—Market conditions may change from time to time, affecting the effectiveness of your risk-to-reward ratio. In very volatile markets, it may be wise to adjust your targets or use wider stop-losses to avoid getting stopped out too often.
Comments